Healthy tiroidja function is vital to overall well-being as the hormones released by this gland impact the functioning of every organ which includes the brain, heart, liver, kidneys, and brain. In this post, we’ll examine the complexities that affect thyroid health, typical conditions, diagnostic techniques, and treatments to help you gain a better understanding of this crucial gland.It is a tiny body organ with a butterfly shape that lies on the neck’s front and plays an important function in controlling various metabolic processes that occur in the body.
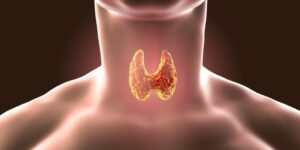
Anatomy and Function of the Tiroidja Gland
The thyroid gland is comprised of two lobes that are connected via a narrow isthmus. It produces three major hormones, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) and the hormone calcitonin. T4 and T3 regulate metabolism in the body, and calcitonin plays a part in the regulation of calcium homeostasis.
Tiroidja Hormone Production and Regulation
Tiroidja hormone production is controlled by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland via an feedback loop that involves the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). When T4 and T3 levels are low, the hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), stimulating the pituitary to release TSH, which in turn stimulates the thyroid gland to produce more hormones.
Common Tiroidja Disorders
Hypothyroidism
The tiroidja gland fails to make sufficient hormones, which results in an increase in metabolic processes. The symptoms of hypothyroidism can include fatigue as well as weight gain, cold intolerance, depression, and dry, flaky skin. The most frequent cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. It’s an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system of the body attacks the thyroid gland.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism manifests itself as an overproduction of thyroid hormones, leading to an increase in metabolism. The symptoms consist of weight reduction, heat intolerance tension, and palpitations. Graves illness, an additional autoimmune disorder, is the most common reason for hyperthyroidism.
Tiroidja Nodules and Cancer
Tiroidja nodules are the result of a mass that develops inside the thyroid gland. Although most nodules are benign, a few can become malignant and lead to thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer symptoms could include a visible lump in the neck area, a hoarse voice, and trouble swallowing.
Diagnosing Tiroidja Disorders
Blood Tests
The blood tests are the most important method of diagnosing thyroid disorders. levels of TSH can be the most accurate test for thyroid function. Other tests assess levels of free T4 levels as well as T3 levels to give a complete picture of the health of the thyroid.
Imaging Tests
Ultrasound is used extensively to assess the thyroid gland’s structure and detect nodules. Tests for radioactive iodine absorption will evaluate thyroid function by determining how much iodine the thyroid absorbs.
Biopsy
The fine needle aspiration biopsy is used to determine if the thyroid nodule is malignant or benign. This method is performed using a fine needle to take cells out of the nodule and then examine them microscopically.
Treatment Options for Tiroidja Disorders
Hypothyroidism Treatment
The most effective remedy for hypothyroidism involves hormone replacement therapy. It is usually using synthesized therroxine (levothyroxine). This medication can restore the normal levels of hormones, easing symptoms and preventing any complications.
Hyperthyroidism Treatment
The treatment options available for patients suffering from hyperthyroidism comprise antithyroid drugs as well as radioactive iodine therapy and surgical procedures. Antithyroid drugs like methimazole and propylthiouracil can reduce the production of hormones. Radioactive iodine therapy eliminates thyroid cells that are overactive, whereas surgery can involve either complete or partial surgical removal of the thyroid.
Thyroid Nodule and Cancer Treatment
The benign thyroid nodules could need to be monitored or removed surgically when they trigger symptoms. Thyroid cancer treatment usually involves surgery, radioactive Iodine therapy and thyroid hormone therapy to reduce TSH levels and prevent the possibility of recurrence.
Lifestyle and Dietary Considerations
Iodine Intake
Iodine intake that is adequate is crucial for healthy thyroid function, since iodine is an essential ingredient in thyroid hormones. Deficiency in iodine can cause hypothyroidism or goiter. The sources of iodine are iodized salt, dairy products, seafood eggs, and seafood.
Nutrient-Rich Diet
A balanced diet that is rich in minerals and vitamins helps support the thyroid’s function. Important nutrients include selenium zinc and vitamin D. Foods like nuts and seeds, whole grains, and leafy green veggies are good for thyroid health.
Regular Exercise
Regular exercise can help reduce weight and improve metabolic health. This is especially important for those who suffer from thyroid issues. Exercise can also help reduce stress which may affect the thyroid’s functioning.
Managing Stress and Tiroidja Health
Chronic stress can negatively affect thyroid function by disrupting the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. Strategies for managing stress like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing techniques may help maintain a healthy hormonal equilibrium and support the health of your thyroid.
Conclusion
The understanding and maintenance of thyroid health is crucial to general well-being. Being aware of the signs and symptoms of thyroid issues and seeking medical attention can result in effective treatment and better health. By incorporating a nutritious lifestyle, regularly exercising, and a stress management program, the individual can maintain their thyroid health and maintain optimal health in their metabolism.